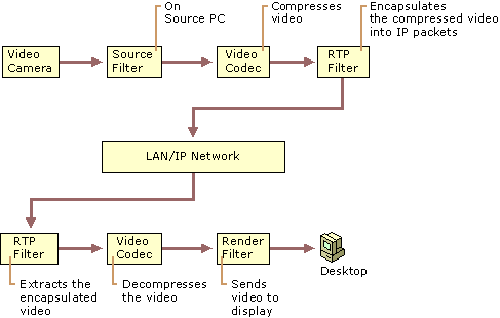
- A video is a moving image having a frame rate minimum 16 frames per second (FPS).
- A video codec is a software which compresses and decompresses the video data. Codec is the short form of "encode" and "decode".
- It means compression is encode and decompression is decode.
- There are several types of video codecs.
H.265/ MPEG-H HEVC codecs:
- x265: A GPL licensed implementation of the H.264 video standard x264 is only a encoder.
H.264/ MPEG-4 AVC codecs:
- x264: A GPL licensed implementation of the H.264 video standard. x264 is only a encoder.
- Nero Digital: Commercial MPEG-4 ASP and AVC codecs developed by Nero AG.
- Quick Time: H.264 implementation released by Apple.
- DivX pro codec: An H.264 decoder and encoder was added in version 7.
H.263/ MPEG-4 codecs:
- DivX Pro Codec: MPEG-4 ASP codec made by DivX, Inc.
- Xvid: Open-source implementation of MPEG-4 ASP, originally based on the open DivX project.
- FF mpeg MPEG-4: Included in the open source libavcodec codec library, which is used by default for decoding or encoding in many open-source video players, frameworks, editors and encoding tools such as Mplayer, VLC, ffd show or Gstreamer. Compatible with other standard MPEG-4 codecs like xvid or DivX pro codec.
H.262/ MPEG-2:
- x262: A GPL licensed implementation of the H.262 video standard x262 is only a encoder.
Microsoft Codecs:
- WMV (Windows Media Video) Microsoft family of proprietary video codec designs including WMC 8, WMC 7 and WMC 9. The latest generation of WMV is standardized by SMPTE as the VC-1 standard.
- MS MPEG-4 v3 created by Microsoft released as a part of Windows Media Tools 4. A hacked version of Microsoft's MPEG-4 v3 codec became known as DivX.
Google (on 2) codecs:
- VP6, VP6-E, VP6-S, VP7, VP8, VP9 propietary high definition video compression formats and codecs developed by On 2 Technologies used in platforms such as Adobe Flash Player 8 and above, Adobe Flash lite, Java FX and other mobile and desktop video platforms. Supports resolution upto 720p and 1080p. VP9 supports resolutions upto 2160p.
- Libtheora: A reference implementation of the Theora video compression format developed by the Xiph.org Foundation, based upon On 2 Technologies VP3 codec, and chriestened by On 2 as the successor in VP3 lineage. Theora is a targeted at competing with MPEG-4 video and similar lower-bitrate video compression schemes.
Applications:
- Video codecs are used in DVD and video CD players and recorders, video broadcast systems, personal computers, and a variety of other applications. In particular, they are transmit video, which may not be feasible with the high data volumes and bandwidths of uncompressed video. For example they are used in operating theaters to record surgical operations.
History:
- Historically video was stored as an analog signal on magnetic tape. Around the time when the compact disc entered into market as a digital-Format replacement of analog audio, it became feasible to also store and convey video in digital form.
- Because of the large amount of storage and bandwidth needed to record and convey raw video, a method was needed to reduce the amount of data used to represent the raw video. Since then, engineers and mathematicians have developed a number of solutions for achieving this goal that involve compressing the digital video data.
Notes: