- An Internet Protocol Address (IP address) is a name in the format of numbers given to every device connected to a network.
- That device use the Internet Protocol for communication.
- IP address serves two principle functions:
- Host or network interface and
- Local Addressing.
- The role of IP address is the name indicates what we seek. Address indicates where it is and route indicates how to get there.
- IP addresses are written and displayed in readable format.
- IP address is designed as 32-bit number which is version 4 (IPv4) which is still using today.
- We have classes in IP addresses based on the range of address.
- Class A, B & C.
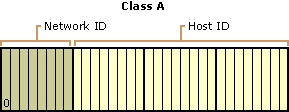
- In class A the first bit of IP address is kept as 0 and range from 1-127.
- In class B two bits are set as 10 and range from 128-191.
- In class C three bits are set to 110 and range from 192-223.
- After the growth of Internet and the shortage of IP addresses a new version of IP (IPv6) using 128 bits for the address was developed in 1995.
| Address Class | First Network ID | Last Network ID |
|---|---|---|
| Class A | 1.0.0.0 | 126.0.0.0 |
| Class B | 128.0.0.0 | 191.255.0.0 |
| Class C | 192.0.0.0 | 223.255.255.0 |
- The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) manages the IP address space allocation globally and delegates the Regional Internet Registries (RIR) to allocate IP address blocks to Internet Service Providers and other entities.
Notes: